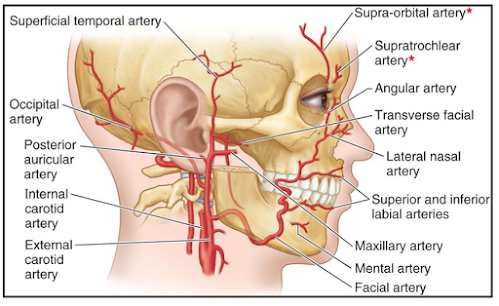
This is the larger terminal branch of the
external carotid artery,
given off behind the neck of the mandible.
It has a wide territory of distribution, and supplies
- 1. The external and middle ears, and the auditory tube
- 2. The dura mater
- 3. The upper and lower jaws and teeth
- 4. The muscles of the temporal and infratemporal regions
- 5. The nose and paranasal air sinuses
- 6. The palate
- 7. The root of the pharynx.
COURSE AND RELATIONS
For descriptive purposes, the maxillary
artery is divided into three parts.
- I. The first (mandibular) part runs horizontally forwards,first between the neck of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, below the auriculotemporal nerve, and then along the lower border of the lateral pterygoid.
- 2. The second (pterygoid) part runs
upwards and forwards superficial to the
lower head of the lateral pterygoid.
- 3. The third (pterygopalatine) part passes between the two heads of the lateral pterygoid and through the pterygomaxillary fissure, to enter the pterygopalatine fossa.
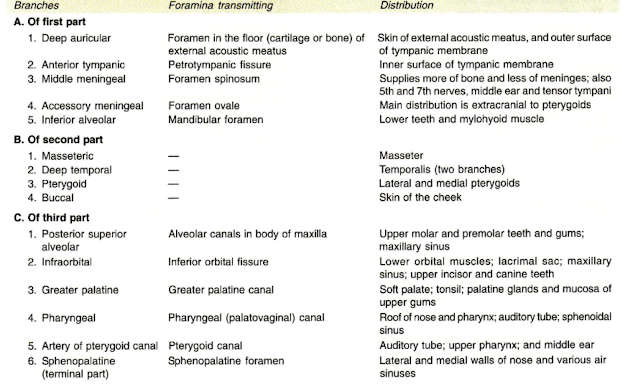
BRANCHES OF FIRST PART OF THE MAXILLARY
ARTERY
- 1. deep auricular artery
- 2. anterior tympanic branch
- 3. middle meningeal artery
- 4. accessory meningeal artery
- 5. inferior alveolar artery
BRANCHES OF SECOND PART OF THE MAXILLARY ARTERY
mainly muscular
- 1. masseteric,
- 2. deep temporal branches - Anterior & Posterior
- 3. to the pterygoid muscles
- 4. buccal branch
BRANCHES OT THIRD PART OF THE MAXILLARY ARTERY
- 1. posterior superior alveolar artery
- 2. infraorbital artery
- 3. greater palatine artery
- 4. pharyngeal branch
- 5. artery of the pterygoid canal
- 6. sphenopalatine artery